Introduction
MS pipe and fittings form the backbone of many industrial systems. As Fortis Forge, we know quality matters. In this guide, we walk you through types, processes, and selection tips. You will gain insight and practical knowledge.
What Are MS Pipes & Fittings?
MS means mild steel, a low carbon steel known for ductility and weldability.
Pipes carry fluids or gases under pressure or gravity.
Fittings elbows, tees, reducers, flanges connect, branch, or change flow direction.
Together, they form piping systems in many industries.

Types of MS Pipe Fittings
The major types include:
Elbows: 90°, 45° to redirect flow
Tees: for branching one line into two
Reducers: to connect different diameters
Couplings / Unions: join straight pipe ends
Flanges: connect pipes or valves, bolted
Caps / Plugs: seal pipe ends
Crosses & Wyes: for multi‑directional branching
Each type plays a unique role in system layout and fluid dynamics.
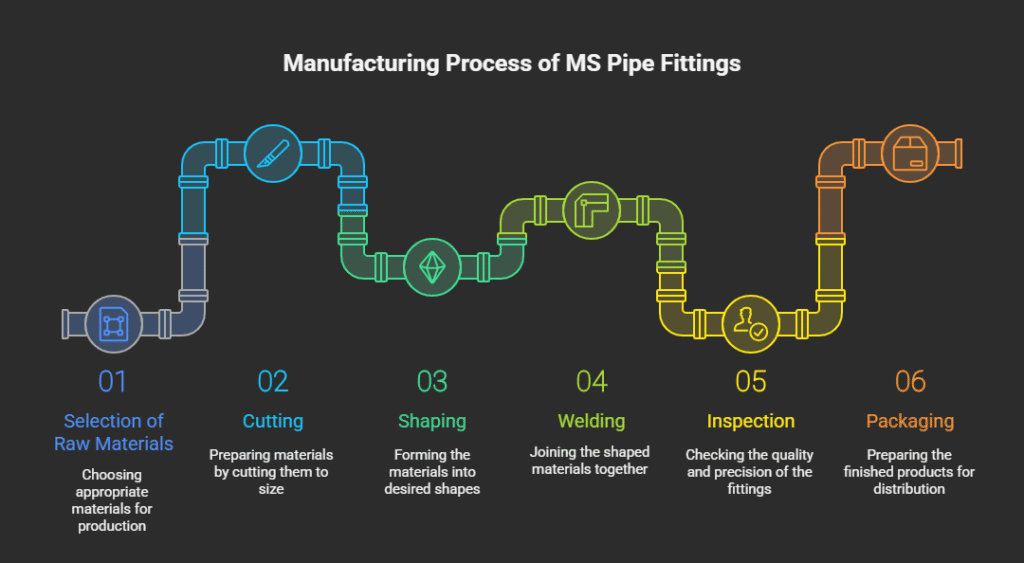
Manufacturing Process & Quality Control
Raw material selection: use certified mild steel billets or pipes.
Cutting / shaping: use saws, laser cutting, or machining.
Forming: bending, forging, or pressing to get shape.
Welding / joining (if required): seam welding or fusion.
Heat treatment / stress relieving: to reduce residual stress.
Machining / finishing: threads, flange surfaces, polishing.
Inspection & testing: dimensional checks, hydrostatic test, non‑destructive tests (NDT).
We enforce strict quality standards to ensure performance and safety.
Applications & Market Demand
MS pipe and fittings are vital in:
Oil & gas pipelines
Power plants (steam, cooling water)
Chemical & petrochemical plants
Fertilizer plants
Water distribution systems
HVAC and fire protection systems
The demand in emerging economies is rising, driven by infrastructure growth.
Selection Criteria & Best Practices
When selecting, consider:
| Factor | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Material grade & certification | Ensures strength and safety under pressure |
| Wall thickness & pressure rating | Must match the system’s design pressures |
| Corrosion resistance / coating | Avoid rust or environmental damage |
| Dimensional accuracy | Prevent leaks or mismatches |
| Weldability / join method | Ease of installation and integrity |
| Cost vs life cycle | Low cost may cost you in downtime |
Best practices:
- Standardize on one grade for easy inventory
- Use spares of critical fittings
- Inspect upon delivery
- Follow proper storage and handling
- Trace and document each batch
Future Trends & Innovations
Corrosion‑resistant coatings (epoxy, galvanizing)
Composite liners or hybrid pipes (steel + polymer)
Smart fittings with sensors to detect leaks
Additive manufacturing for custom fitting shapes
Sustainability focus: use greener steel, reduce waste
These trends will shape the future of MS pipe systems.
Case Study / Fortis Forge Advantage
At Fortis Forge, we combine technical expertise and quality control.
We follow ISO, ASTM, and ASME standards
Our plant uses state‑of‑the‑art machinery
We partner with clients early to design custom fittings
We ensure delivery, technical support, and after sales
Share a real client example (if available): how Fortis Forge solved a complex piping challenge.

Conclusion
MS pipe and fittings remain foundational in industrial infrastructure.
If you select well, maintain properly, and plan smartly, your system works reliably.
Fortis Forge commits to quality, innovation, and service.
Contact us to discuss your piping needs.
